
Generating power from the sun is all about harnessing the sun's energy and converting that energy into usable electricity. The idea is far from new, but it's only in recent years that the technology has been good enough to make the most of the limited daylight we get in the UK.
To harness the power of the sun we fit solar panels (known as photovoltaic panels) to the part of your roof which faces the sun the most. These panels convert the energy from the sun into a DC current which is then fed into a converter. The converter converts the DC current to a mains voltage AC current (there are safety switches placed on both sides of the inverter allowing any component to be safely isolated for servicing).
The AC current generated by your solar panels is fed through a 'generation meter' into the main household fuse box board. The generation meter is the thing that records the total amount of electricity generated and this is what you get paid on for the feed-in tariff (FIT).
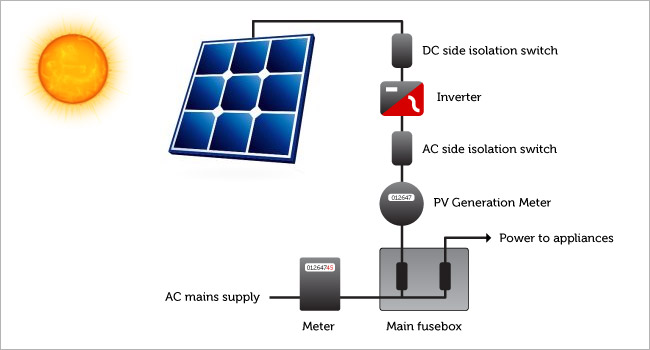
From the distribution board the electricity is either used by the lights, electrical goods or domestic appliances in your home, or it's fed back into the national grid through a two way meter (or two separate meters). These meters record the amount of electricity you take from the grid, and the amount of electricity you export into the grid - it is this export meter that records what you sell to the electricity supply companies.
Of course, the above is a cut down summary of how solar panels work. If you would like to know more, please call us on 0800 044 3045 or request a free survey.